Plugins can be mounted into the KDB and can access or manipulate the KeySet on every access.
Multiple plugins can be mounted into the key data base. On every access to the key data base they are executed and thus can change the functionality.
Introduction
Elektra already has a wide range of different plugins. The plugin folders should contain a README.md with further information. (Or follow links below.) The plugins are:
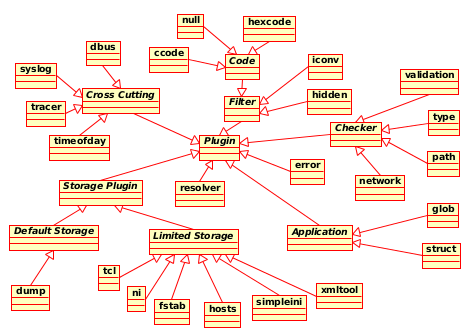
For background information see elektra-plugins-framework(7).
C-Interface
All plugins implement the same interface:
kdbOpen()callselektraPluginOpen()of every plugin to let them do their initialisation.kdbGet()requestselektraPluginGet()of every plugin in the queried backends to return a key set.kdbSet()usually callselektraPluginSet()of every plugin in the queried backends to store the configuration.kdbSet()also callselektraPluginError()for every plugin when an error happens. Because ofelektraPluginError(), plugins are guaranteed to have their chance for necessary cleanups.kdbClose()makes sure that plugins can finally free their own resources inelektraPluginClose().
KDB-Interface
- To list all plugins use kdb-list(1).
- To check a plugin use kdb-check(1).
- For information on a plugin use kdb-info(1).
- For mount plugin(s) use kdb-mount(1).
See also
For an easy introduction, see this tutorial how to write a storage plugin. For more background information of the plugins framework, continue here. Otherwise, you can visit the the API documentation.
Plugins
Resolver
Before configuration is actually written, the file name needs to be determined (will be automatically added by kdb mount):
- resolver uses POSIX APIs to handle conflicts gracefully
- wresolver minimalistic resolver for non-POSIX systems
- noresolver does not resolve, but can act as one
and afterwards the configuration file must be synced with harddisc (recommended to add at every kdb mount):
- sync uses POSIX APIs to sync configuration file with harddisc
Storage
Are responsible for reading writing the configuration to configuration files.
Read and write everything a KeySet might contain:
- dump makes a dump of a KeySet in an Elektra-specific format
Read (and write) standard config files of /etc:
- augeas parses and generates many different configuration files using the augeas library
- hosts read/write hosts files
- line reads any file line by line
Using semi-structured data for config files:
- tcl-like config files (including meta data).
- ni parses INI files based on ni.
- ini parses INI files based on inih.
- xmltool uses XML.
- yajl uses JSON.
Plugins that just show some functionality, (currently) not intended for productive use:
- fstab reads fstab files.
- regexstore
- simpleini is ini without sections
- csvstorage for csv files
System Information
Information compiled in Elektra:
- version is a built-in plugin directly within the core so that it cannot give wrong version information
- constants various constants, including version information
Providing information found on the system not available in persistent files:
- uname information from the uname syscall.
Filter
Filter plugins process keys and their values in both directions. In one direction they undo what they do in the other direction. Most filter plugins available now encode and decode values. Storage plugins that use characters to separate key names, values or metadata will not work without them.
- cachefilter stores filtered keys internally so that they do not get accidentally lost and can be written to the storage again without the user having to remember including them in the writeout
Encoding
Rewrite unwanted characters with different techniques:
Transformations:
Doing other stuff:
- crypto encrypts / decrypts confidential values
- iconv make sure the configuration will have correct character encoding
- hidden hides keys whose names start with a
.. - null takes care of null values and other binary specialities
Notification and Logging
Log/Send out all changes to configuration to:
Debug
Trace everything that happens within KDB:
Checker
Copies meta data to keys:
- glob using globbing techniques
- struct using a defined structure (may also reject configuration not conforming to that structure)
- spec copies metadata from spec namespace Plugins that check if values are valid based on meta data (typically copied by another plugin just before):
- validation by using regex
- network by using network APIs
- path by checking files on filesystem
- type using runtime type checking (CORBA types/)
- enum compares the keyvalue against a list of valid values
- mathcheck by mathematical expressions using keysvalues as operands
- conditionals by using if-then-else like statements
Interpreter
These plugins start an interpreter and allow you to use a bindings.
- jni java plugins started by jni, works with jna plugins
- python Python 3 plugins
- python2 Python 2 plugins (deprecated)
- lua Lua plugins
Others
- doc contains the documentation of the plugin interface
- error yields errors as described in metadata (handy for test purposes)
- template to be copied for new plugins
- lineendings tests file for consistent line endings
- list loads other plugins
- filecheck does sanity checks on a file
- iterate iterate over all keys and run exported functions on tagged keys
- dpkg reads /var/lib/dpkg/{available,status}
- curlget fetchs configuration file from a remote host
- shell executes shell commandos after kdbGet, kdbSet and kdbError
- semlock a semaphore based global locking logic
- profile links profile keys
New Plugins
To add a new plugin you can copy the template plugin. Please make sure to add your plugin:
- to this list, at least in Others
- to cmake, at least in ALL
 1.8.8
1.8.8